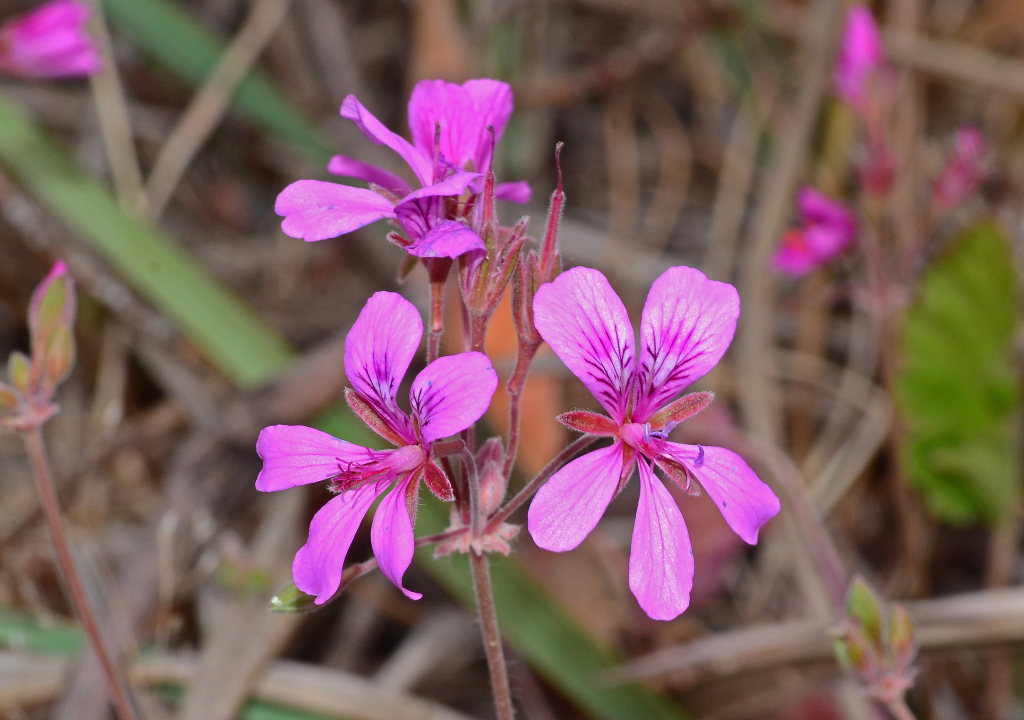
Pelargonium rodneyanum
Lindl. Magenta Stork's-billTufted, erect perennial to c. 40 cm high; stems, peduncles and pedicels with short glandular hairs and scattered longer eglandular hairs; roots tuberous. Leaves all or mostly basal; cauline leaves, if present, opposite or branch-opposed, lamina ovate-cordate or ovate, 2–5.5 cm long, 1.5–5 cm wide, entire to shallowly 5–7-lobed, sparsely pubescent to glabrescent, usually pilose along veins beneath, margin crenate; petioles c. 3–7(–12) cm long. Umbels 2–7-flowered; peduncles 5–12(–25) cm long, often arising from base of plant; pedicels 10–30 mm long; sepals narrowly ovate, 5–8 mm long, acute, shortly pubescent, often with scattered longer and/or coarser hairs; sepal spur (3–)5–9 mm long; petals obovate to oblong, 12–17(–20) mm long, deep rosy-magenta, sometimes veined or blotched darker; fertile stamens 7 or 8. Fruits 16–25 mm long; meri-carps pilose. Flowers Nov.–May.
LoM, MuM, Wim, GleP, VVP, VRiv, GipP, OtP, Gold, CVU, GGr, DunT, EGL, HSF, HNF, VAlp. Also SA, NSW. Rather common west of Melbourne, usually growing on fertile clays or loams in grassland or woodland communities, but also on rocky outcrops, scattered and rather uncommon in the east.
Smith, L.P.; Walsh, N.G. (1999). Pelargonium. In: Walsh, N.G.; Entwisle, T.J., Flora of Victoria Vol. 4, Cornaceae to Asteraceae, pp. 233–236. Inkata Press, Melbourne.
 Spinning
Spinning