Cynoglossum australe
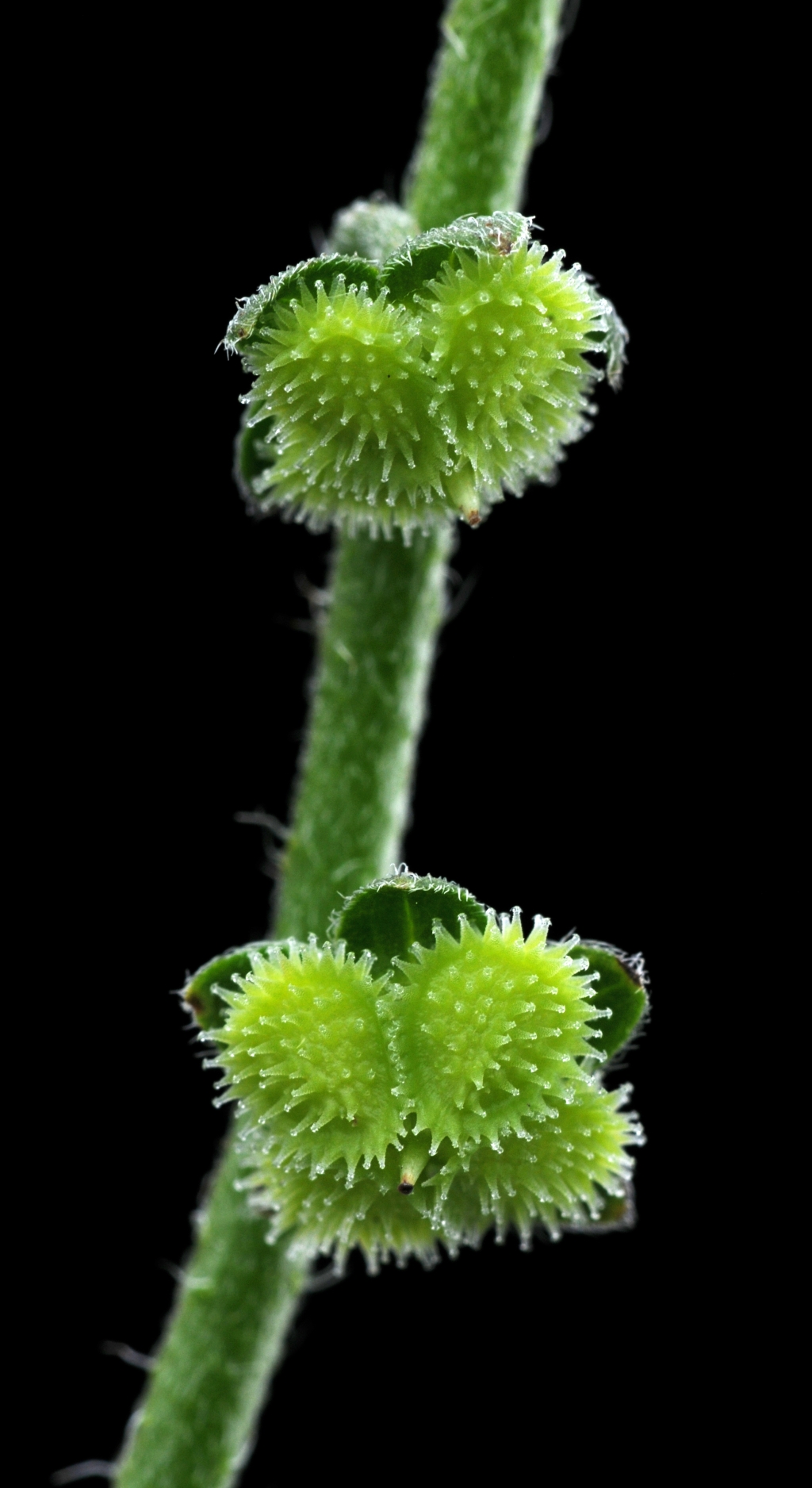
R.Br. Australian Hound's-tongueHerb mostly to c. 75 cm (rarely to 1.2 m) high. Basal leaves lanceolate to oblanceolate, 6–20 cm long, 10–35 mm wide; petiole 2–10 cm long; stem leaves lanceolate, decreasing in size towards inflorescence, apex acute, base cuneate, margins usually flat, sessile. Bracts absent or rarely subtending lower 1 or 2 flowers. Pedicels 2–5 mm long; sepals c. triangular, 2–3 mm long, obtuse or rounded, connate in basal third to half, elongating with age; corolla 3–6 mm long, glabrous except for papillose 2-lobed scales in throat, white, blue or rarely pink, tube slightly longer than the obtuse lobes; anthers to c. 1 mm long, with a mucronate appendage; style c. 1.5 mm long. Mericarps saucer-shaped, 2.5–3.5 mm long, with a raised winged rim, pale brown or yellowish-brown; spines on margin of rim and variously arranged on upper and lower surfaces of mericarp. Flowers mainly Sep.–Feb.
LoM, MuM, Wim, GleP, Brid, VVP, VRiv, RobP, GipP, OtP, WaP, Gold, CVU, GGr, DunT, NIS, EGL, EGU, WPro, HSF, HNF, OtR, Strz, MonT, HFE, VAlp. All States. Widespread in a diverse range of habitats through much of the State, often abundant in disturbed sites or following fire.
The var. drummondii was based on material with few spines on the face of the mericarps. The ornamentation of the mericarps, however, is quite variable and no clear discontinuities in this character are evident from the specimens examined.
Jeanes, J.A. (1999). Boraginaceae. In: Walsh, N.G.; Entwisle, T.J., Flora of Victoria Vol. 4, Cornaceae to Asteraceae, pp. 387–411. Inkata Press, Melbourne.
 Spinning
Spinning