Crassula exserta
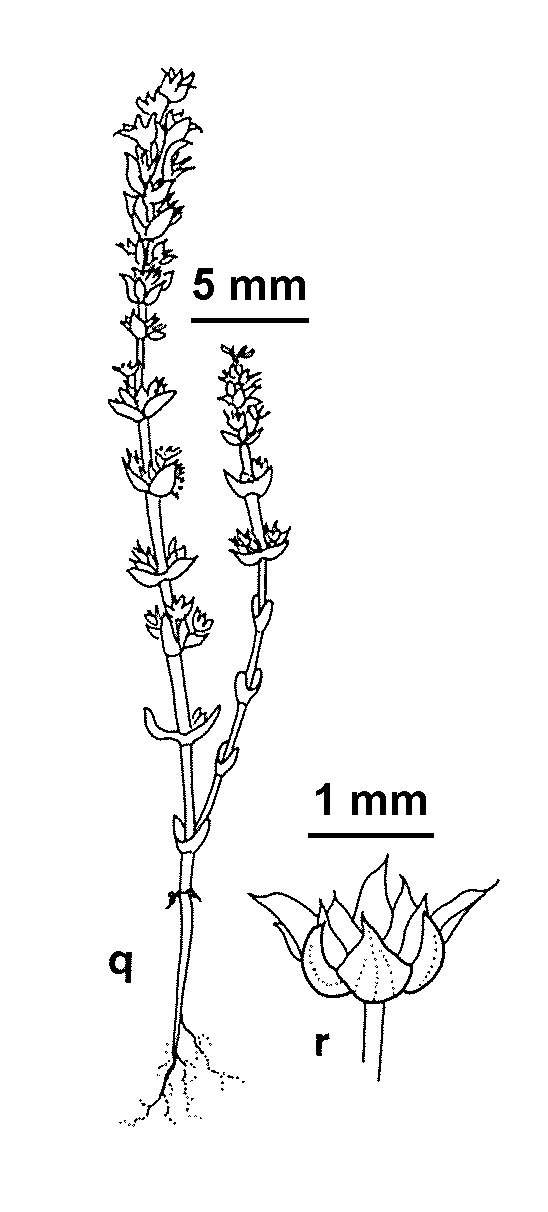
(Reader) Ostenf. Large-fruit CrassulaAnnual with stiffly erect stem to 15 cm, little-branched and mainly from the fourth to sixth nodes. Leaves ovate to elliptic, 0.8–3.2 mm long, 0.6–1.8 mm wide, usually obtuse, almost flat above, strongly convex below, papillose to smooth. Inflorescence 1–several thyrses with sessile dichasia subtended by leaf-like bracts. Flowers 4- or 5-merous; calyx-lobes lanceolate, 1–1.5 mm long, pointed, incurving between follicles; corolla white tinged red; lobes linear-lanceolate, 1.4–1.7 mm long, acute or pointed; nectary scales linear, 0.4–0.5 mm long, c. 0.1 mm wide, rounded to truncate; carpels almost cylindric, with 2 ovules. Follicles slightly reclined, tuberculate, releasing seeds through apical pore or detaching basally from receptacle; fruiting pedicel rarely to 5 mm long; seeds 2.4–2.8 mm long, smooth. Flowers Aug.–Nov.
LoM, MuM, Wim, MSB, RobP, Gold, GGr, DunT. Also WA, SA, Tas. (Flinders Is.). Grows usually in sandy or gravelly clay soils in the west and northwest of the state but rather uncommon, often occurring with C. colorata and/or C. sieberiana.
Characterized by its star-shaped fruit produced by the reclining follicles that are held in place by the incurved calyx-lobes. Superficially similar fruit occur in some forms of C. sieberiana, a species distinguished by its smooth follicles, which are shorter than the petals and opened to the base.
Toelken, H.R.; Jeanes, J.A.; Stajsic, V. (1996). Crassulaceae. In: Walsh, N.G.; Entwisle, T.J., Flora of Victoria Vol. 3, Dicotyledons Winteraceae to Myrtaceae, pp. 542–555. Inkata Press, Melbourne.
 Spinning
Spinning

