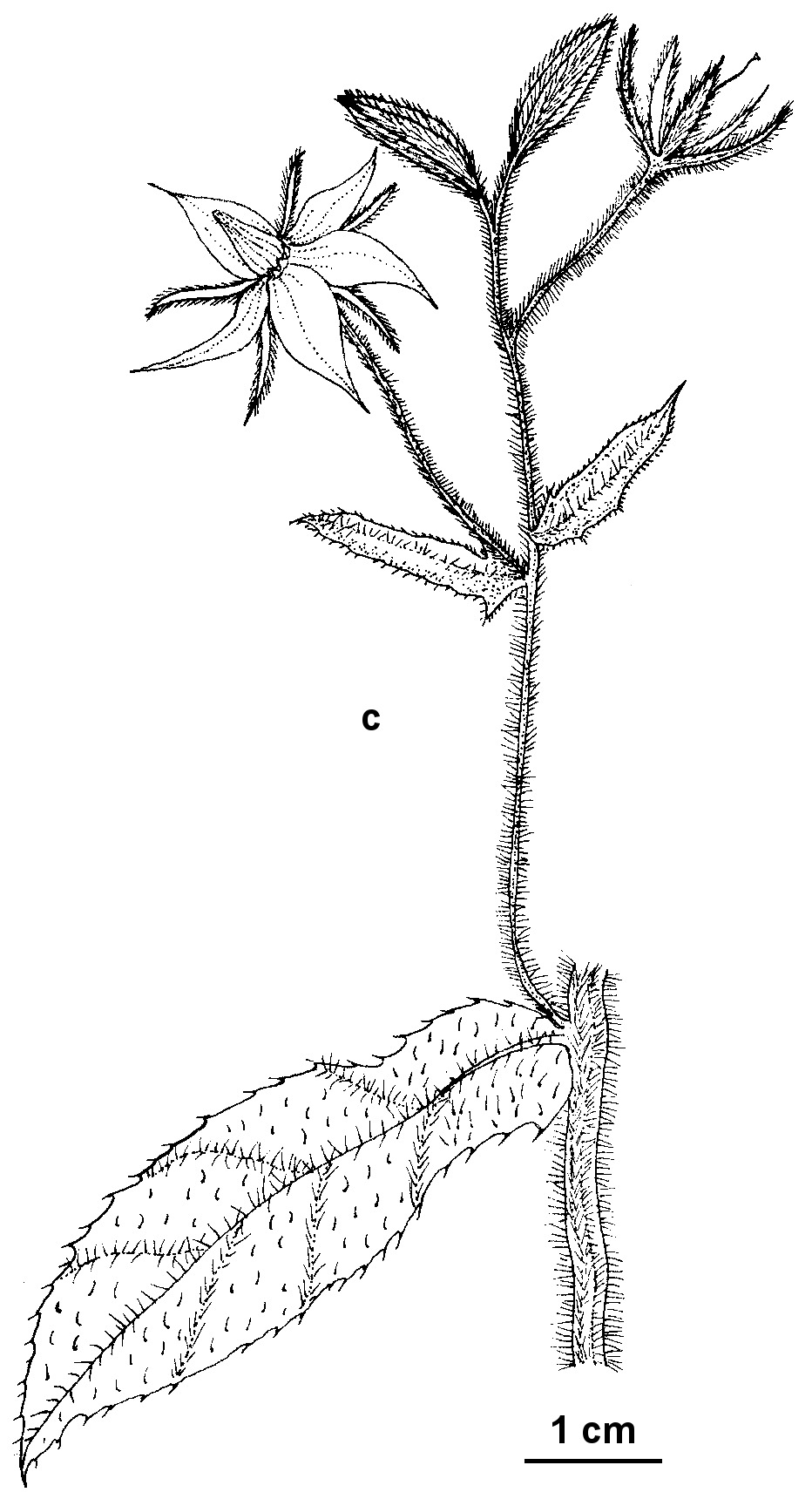
Borago
Erect annual or perennial herbs, much-branched, all parts usually hispid; basal rosette present initially, soon obscured. Leaves initally opposite and petiolate, becoming alternate and sessile, margins irregular. Inflorescences terminal, consisting of few–many scorpioid cymes; bracts present. Flowers pedicellate; sepals 5, connate basally, scarcely elongating after flowering; corolla regular, 5-lobed, rotate (in Victoria) or campanulate, with a short tube, blue; scales in throat saccate; stamens exserted or included in throat of corolla-tube, each with an erect exterior appendage, anthers linear, almost sessile, exposed above corolla-tube forming an erect column around the style, appendages small; ovary 4-lobed, 4-celled, with a nectary scale around each cell, style inserted at base, filiform, shorter than anthers at anthesis, stigma minute. Fruit breaking into 4 hard mericarps leaving an insignificant central gynobase; mericarps erect, ridged, smooth or muricate, with a longitudinal keel; basal attachment scar with a raised rim.
3 species, mainly from Europe and the Mediterranean region but also extending to Asia; 1 species naturalised in Australia.
Jeanes, J.A. (1999). Boraginaceae. In: Walsh, N.G.; Entwisle, T.J., Flora of Victoria Vol. 4, Cornaceae to Asteraceae, pp. 387–411. Inkata Press, Melbourne.
 Spinning
Spinning


