Borago officinalis
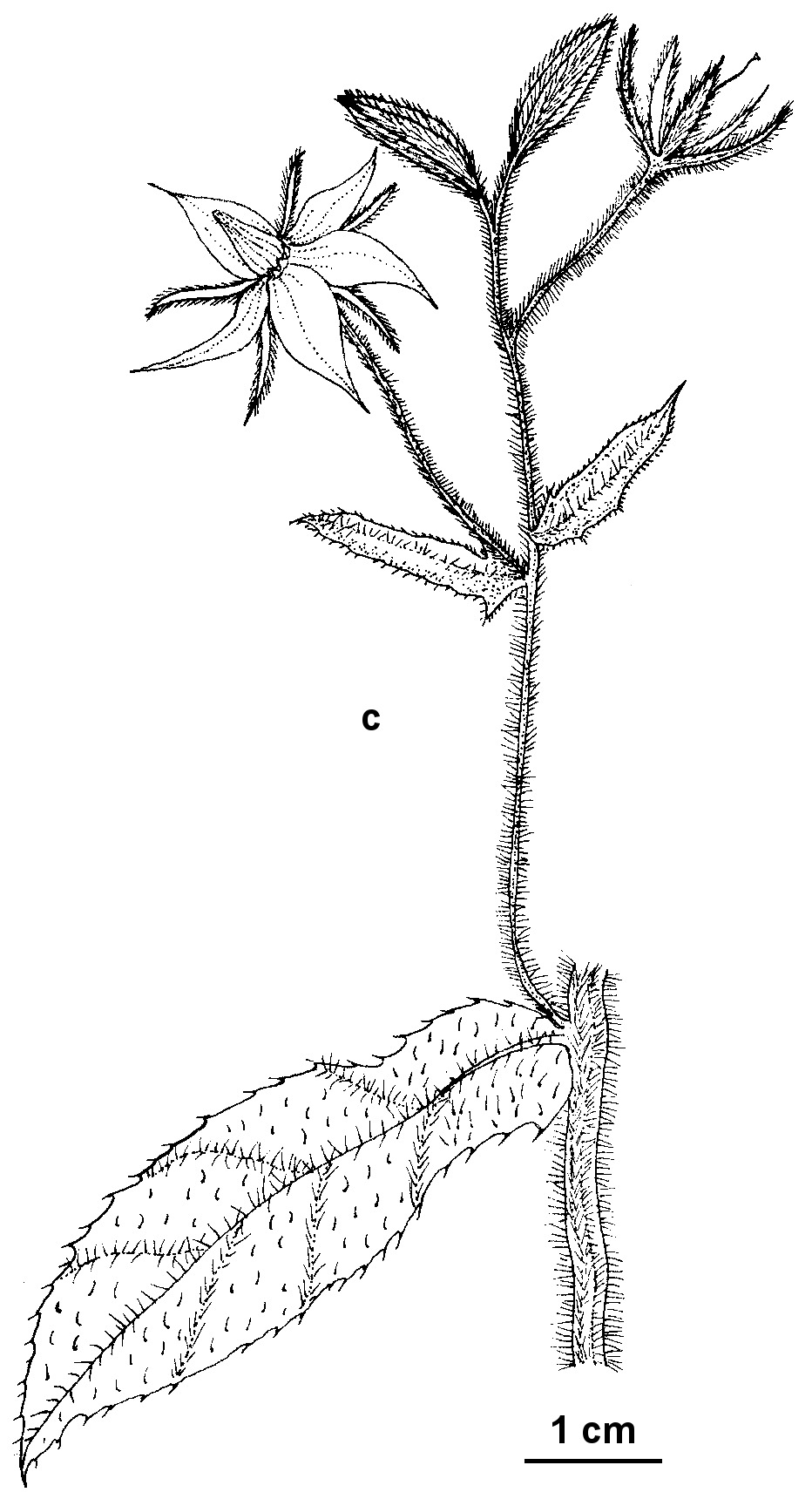
L. BorageAnnual herb 30–80 cm high; hairs dense, simple, spreading, the larger ones broad-based. Leaves elliptic to lanceolate or oblanceolate, 4–20 cm long, 2–7 cm wide, acute or obtuse, base cuneate with decurrent clasping lobes, margins undulate, upper surface c. evenly hispid, hairs mainly confined to veins beneath. Inflorescences many-flowered; bracts shorter than pedicels; pedicels 10–40 mm long. Flowers 15–25 mm diam., deep blue; calyx 8–15 mm long, lobes narrow-elliptic to linear, connate for up to one-third of their length; corolla 12–18 mm long, tube short, lobes elliptic, throat scales conspicuous, hairy; stamen filaments 1–2 mm long, appendage c. 3 mm long, anthers 5–7 mm long, dark, tipped with a short apiculate appendage; style 5–7 mm long. Mericarps oblong-obovoid, c. 6 mm long, wrinkled, pale to dark brown. Flowers Aug.–Dec.
VVP, VRiv, GipP, CVU, EGL, HSF, HNF, Strz. Also naturalised WA, SA, NSW, Tas. Native to southern Europe. Cultivated as a culinary herb and occasionally escaping or persisting in abandoned gardens, usually in moist sites.
Jeanes, J.A. (1999). Boraginaceae. In: Walsh, N.G.; Entwisle, T.J., Flora of Victoria Vol. 4, Cornaceae to Asteraceae, pp. 387–411. Inkata Press, Melbourne.
 Spinning
Spinning