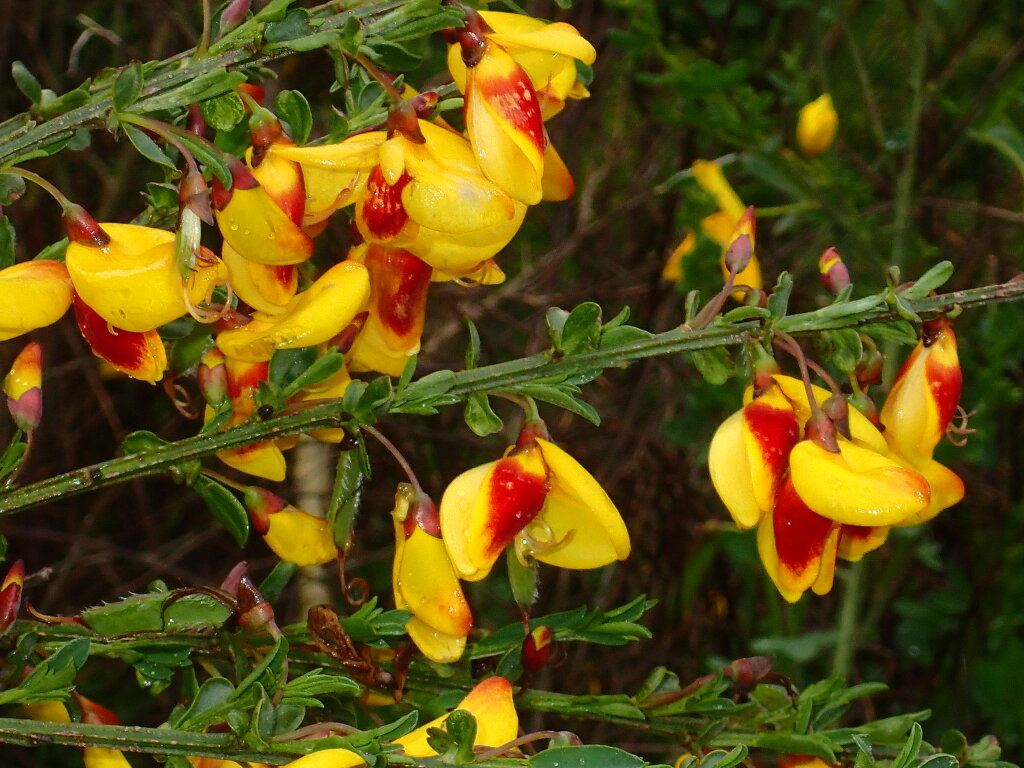
Cytisus scoparius
(L.) Link English BroomErect, ascending or procumbent shrub to 2.5 m tall; stems numerous, glabrescent, 5-angled. Leaves trifoliolate and shortly petiolate on lower stems, 1-foliolate and subsessile higher up, or absent; leaflets narrow-elliptic to obovate, 5–20 mm long, 1.5–8 mm wide, sessile, pubescent, apex acute or obtuse; stipules inconspicuous. Flowers 1 or 2 per leaf-axil, arranged in long terminal raceme; pedicels slender, 5–12 mm long; calyx c. 6 mm long, glabrous, lower lip longer than upper; corolla mostly 16–20 mm long, golden-yellow, sometimes with reddish-brown markings; standard broad, notched. Pod linear-oblong, 25–60 mm long, 8–10 mm wide, ciliate; seeds mostly 6–18, more or less elliptic, c. 3 mm long, compressed, green-yellow; aril yellow. Flowers mainly Sep.–Dec.
Wim, GleP, VVP, VRiv, GipP, OtP, Gold, CVU, GGr, DunT, HSF, HNF, OtR, Strz, VAlp. Also naturalised WA, SA, NSW, ACT, Tas . Native to Europe. A garden or hedge plant that has become widely established throughout higher rainfall parts of the State. It readily invades disturbed areas such as roadsides, fence-lines and grazing land and will establish itself in bushland particularly along watercourses.
Declared a noxious weed in Victoria, English Broom is particularly troublesome and proving difficult to eradicate. It has become firmly entrenched in a number of areas of the state where it is a severe threat to native bushland.
Jeanes, J.A. (1996). Fabaceae. In: Walsh, N.G.; Entwisle, T.J., Flora of Victoria Vol. 3, Dicotyledons Winteraceae to Myrtaceae, pp. 663–829. Inkata Press, Melbourne.
 Spinning
Spinning