Salix ×sepulcralis
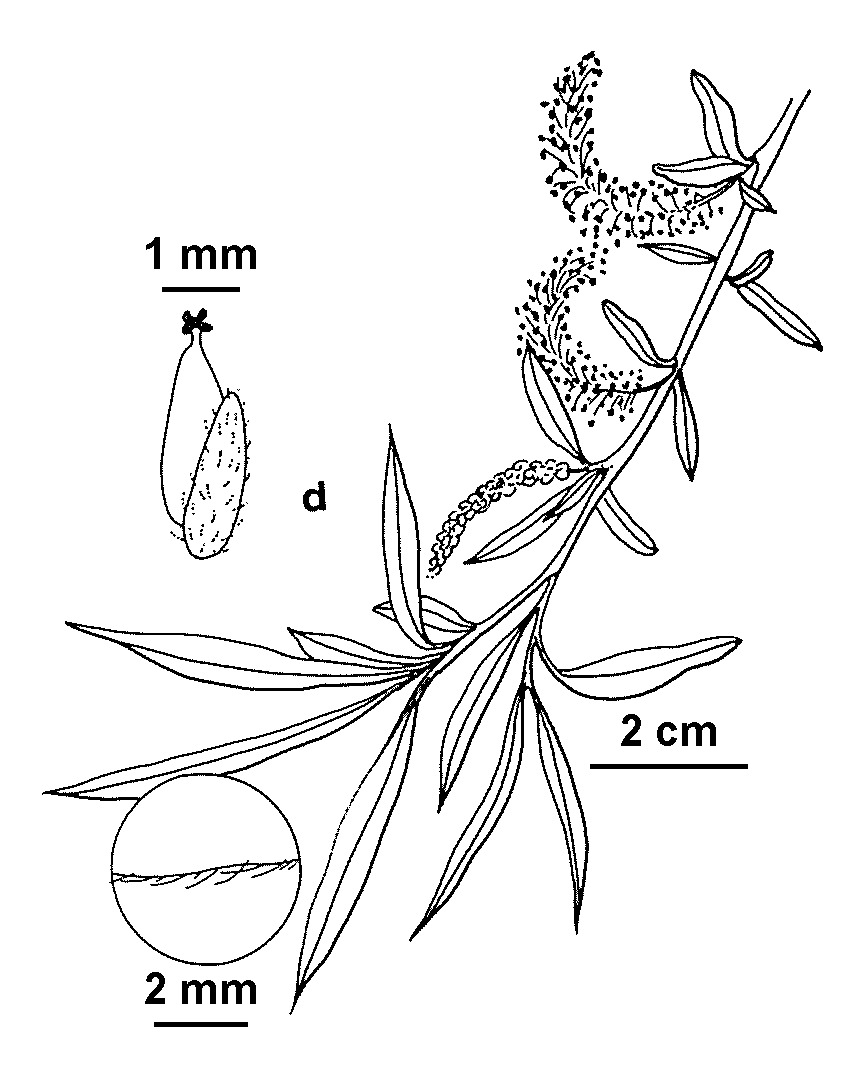
Simonk.Weeping trees to 18 m or more high, trunks 1-several, crown often wider than high; bark grey-brown to dark brown, ultimately moderate fissured; outer branches, twigs and shoots weeping, moderately to very long-pendulous but only the shoots c. vertical; twigs very slender, not fragile, at first thinly appressed-villous, soon glabrescent, golden to greenish-yellow or brownish-green; buds rich brown, glabrous or somewhat pubescent. Leaves narrow-lanceolate, 7–18.5 cm long, 0.8–2.9 cm wide, soon glabrous, dark green above, glaucous or glaucescent beneath; apex acuminate; base cuneate or slightly rounded; margins finely glandular-serrate; petioles usually with 1–several dark brown sessile glands on either side from well below apex to the apex; stipules caducous, narrowly ovate-acuminate, to 4 mm long, margins glandular-serrate, usually with scattered sessile glands on upper surface. Catkins male, female, or not infrequently, androgynous, produced on short leafy lateral shoots, dense-flowered, narrowly tapered-cylindric, often curved, 1.5–5 cm long, 0.5–1 cm wide; peduncle 1–5 mm long; catkin-scales caducous, pale yellow, oblong-ovate, 2–3.5 mm long; stamens 2; ovary shortly flask-shaped, sessile or very shortly stalked, glabrous, 1.8–2.5 mm long; capsules 4–6 mm long.
VVP, GipP, OtP, HSF.
2 varieties naturalised in Victoria.
 Spinning
Spinning