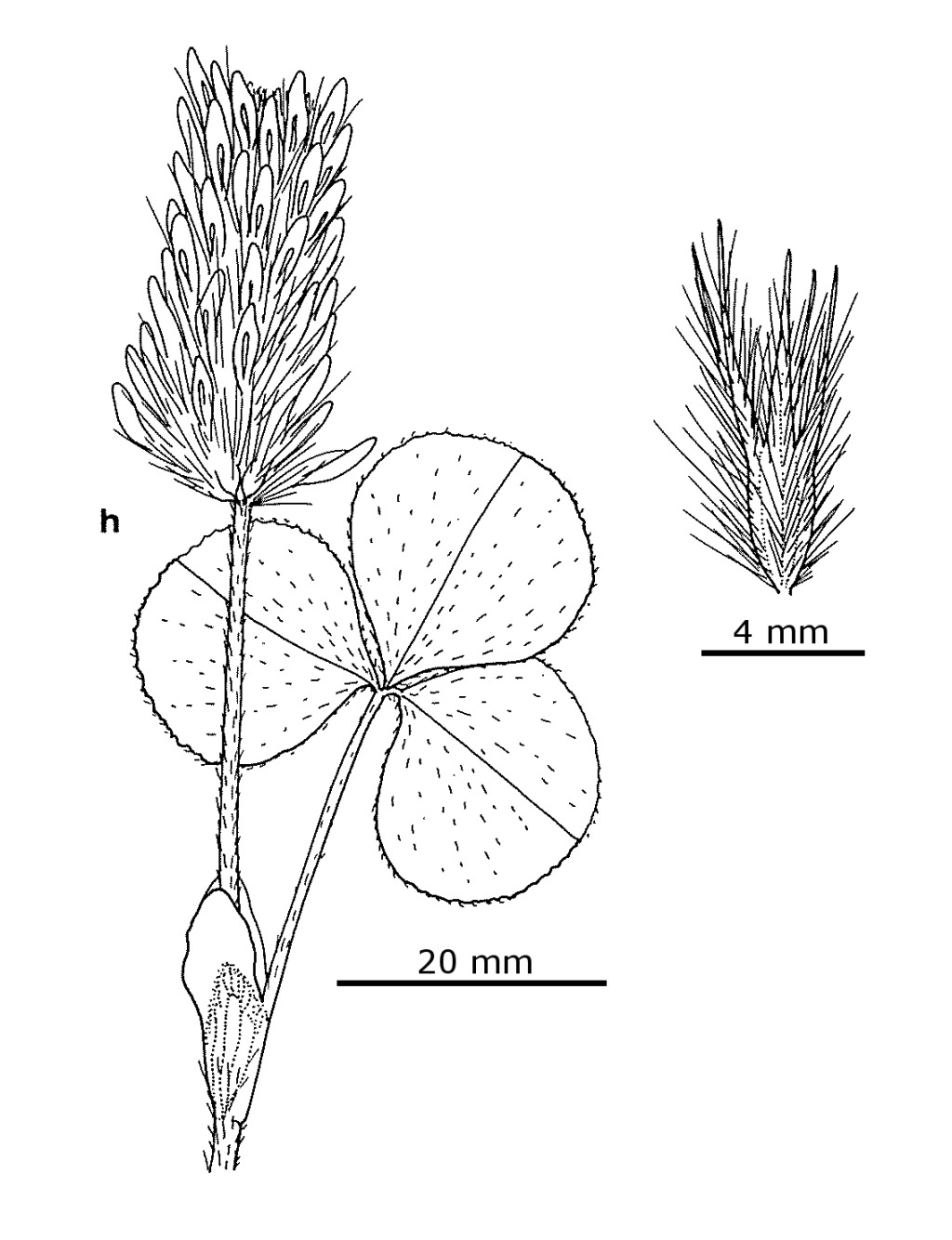
Trifolium incarnatum var. incarnatum
Crimson CloverErect or ascending annual herb; stems few, 20–50 cm long, simple or scarcely branching from base, villous. Leaves palmately trifoliolate, short-to long-petiolate; leaflets obovate, 10–28 mm long, 10–20 mm wide, appressed-hairy, finely toothed on upper margins, apex rounded or retuse; stipules membranous, veined, hairy, adnate to petioles for three-fifths of their length. Inflorescence many-flowered, terminal, ovoid to cylindric, 20–60 mm long, 10–15 mm wide, pedunculate; flowers sessile. Calyx c. 10 mm long, covered with long appressed hairs, tube cylindric, 10-veined, throat narrowed by an annular thickening in fruit, teeth 1–2 times as long as tube, equal to subequal, spiny, spreading in fruit; corolla 10–14 mm long, red to purple, rarely cream, not persistent; standard oblong-elliptic, acute. Pod ovoid, c. 3 mm long, membranous, exserted from calyx tube; seed 1, ovoid, c. 2 mm long, green-yellow. Flowers mainly Oct.–Dec.
MuM, Wim, VVP, VRiv, GipP, OtP, CVU, HNF. Also naturalised WA, SA, NSW, ACT, Tas. Native to south-eastern Europe.
Reported mainly from the north and west of the State and on the Mornington Peninsula near Melbourne.
Zohary & Heller (1984) recognize 2 varieties, apparently only the type variety occurring in Victoria.
Jeanes, J.A. (1996). Fabaceae. In: Walsh, N.G.; Entwisle, T.J., Flora of Victoria Vol. 3, Dicotyledons Winteraceae to Myrtaceae, pp. 663–829. Inkata Press, Melbourne.
 Spinning
SpinningZohary M.; Heller, D. (1984). The genus Trifolium. Israel Academy of Sciences and Humanities, Jerusalem.

