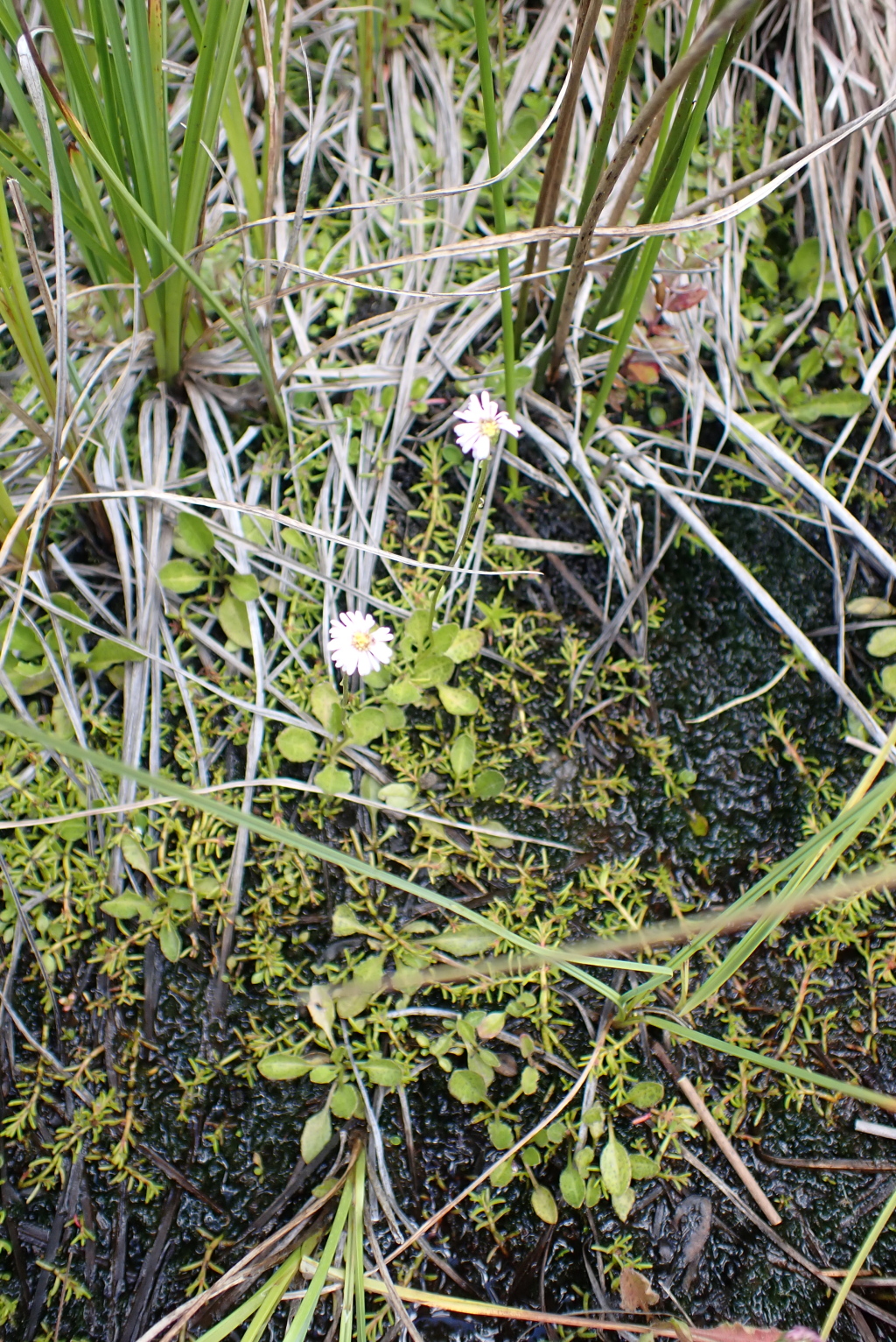
Lagenophora montana
Hook.f.Roots fibrous, produced at intervals from slender spreading rhizomes (to c. 0.5 mm diam. when dry). Leaves loosely rosetted, sometimes borne on lower (up to c. 10 cm) stem and grading into bracts; leaves up to c. 50–70 mm long and c. 15 mm wide (but often smaller), obtuse to broadly acute, hirsute to almost glabrous, almost entire to shallowly dentate with 2–4 pairs of teeth, the teeth and apex often scarcely apiculate. Scape 9–16(–25) cm long, bearing a few small narrow bracts to c. 10 mm long, almost glabrous except for appressed hairs below the capitulum and sometimes a few spreading hairs elsewhere; capitulum c. 3–5 mm wide; involucral bracts mostly narrowly oblong, to 3 mm long, obtuse to sub-acute. Ray florets ca. 68, ligules 2.8–3.8 mm long, white, mauve or purplish. Disc florets c. 20, yellow. Cypselas oblanceolate, c. 2–3.5 mm long and 0.8–1 mm wide, brown or purplish with paler margins; beak to c. 0.5 mm long. Flowers mostly summer.
VVP, Gold, CVU, EGL, HSF, HNF, VAlp. Also NSW, Tas. New Zealand. Localized in damp montane habitats such as swamps, boggy herbfields, riparian scrub or open treeless areas east of Daylesford, with an outlying occurrence in the west at Mt Buangor.
This species has been overlooked or sometimes relegated to synonymy or varietal rank under Lagenophora stipitata, but the numerous recent collections at MEL form as distinctive a taxon as the other Victorian species of Lagenophora. Plants generally form small colonies.
Clarke, I.C. (1999). Lagenophora. In: Walsh, N.G.; Entwisle, T.J., Flora of Victoria Vol. 4, Cornaceae to Asteraceae, pp. 864–867. Inkata Press, Melbourne.
 Spinning
Spinning