Platylobium montanum
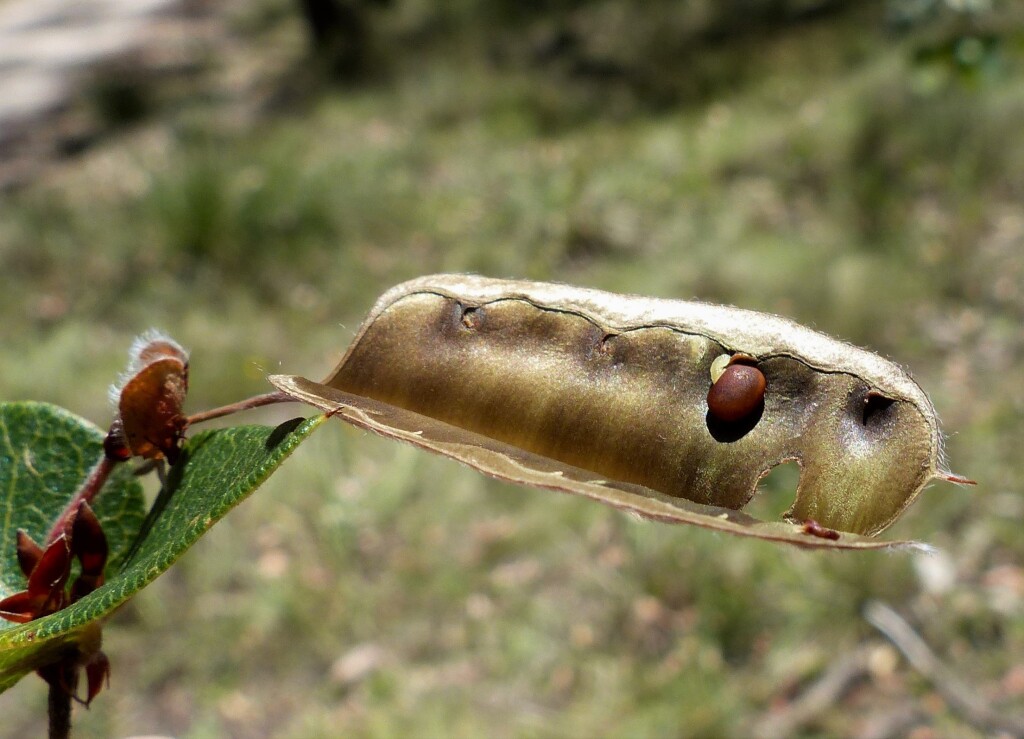
I.Thomps.Prostrate, trailing, scrambling or weakly erect shrubs to 2 m high; stems glabrous to densely pubescent. Leaves opposite (occasionally some alternate), unifoliolate; petiole 2–15 mm long; lamina broadly ovate to ovate, 2–5 cm long, 1.5–4 cm wide, base cordate, occasionally truncate or rounded, apex ± acute, apiculate. Flowers 1–4 per axil; pedicels distinct, exserted from basal bracts and scales; bracteoles convex, 4–10 mm long, overlapping lower half of calyx, brown or reddish-brown, usually obscurely striate, glabrous or with scattered hairs; calyx with scattered to dense appressed hair, upper lobes 5–8(–10) mm long (including tube), lower lobes 3–5.5 mm long; ovary pubescent throughout or on margins or part of valves, occasionally entirely glabrous. Pod with thin wing 1–2(–3) mm wide beyond the upper sutural nerve, usually pubescent.
Wim, VVP, VRiv, GipP, Gold, CVU, GGr, EGL, WPro, HSF, HNF, Strz, VAlp.
2 subspecies in Victoria.
Previously included in a broadly defined P. formosum. This species complex has been revised, and is now represented by 6 species (P. formosum, P. rotundum, P. montanum, P. infecundum, P. parviflorum, and P. reflexum). Platylobium formosum sensu stricto is restricted to New South Wales and Queensland. The other five species occur in Victoria (Thompson 2011).
 Spinning
SpinningThompson, I.R. (2011). A revision of Platylobium (Fabaceae: Bossiaeeae). Muelleria 29: 154–172.