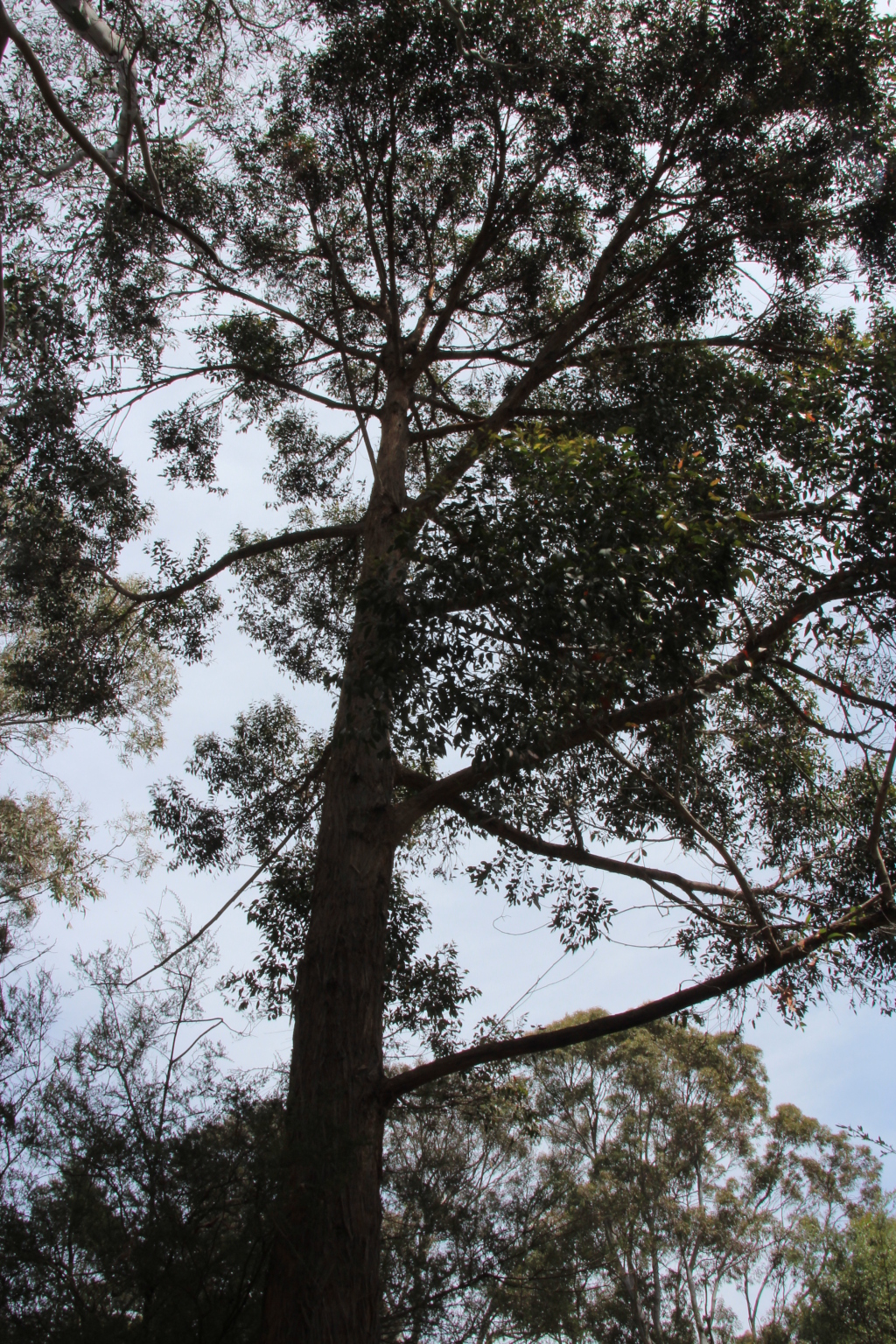
Eucalyptus globoidea
Blakely White StringybarkTree to 40 m tall; bark rough to small branches, stringy. Juvenile leaves petiolate, opposite for few pairs then alternate, ovate, undulate, scabrous above and below for many nodes, to 10.5 cm long, 6 cm wide, green; adult leaves petiolate, broadly lanceolate to lanceolate, 7.5–12 cm long, 1.2–2.5 cm wide, concolorous, glossy, green; reticulation sparse, with numerous island oil glands. Inflorescences axillary, unbranched; peduncles to 1.2 cm long, 11–15-flowered; buds more or less sessile, fusiform, to 0.6 cm long, 0.4 cm diam., no scar (single operculum); operculum acutely conical; stamens irregularly flexed; anthers dorsifixed, reniform; ovules in 2 vertical rows; flowers white. Fruit sessile, hemispherical to truncate-globose, to 0.7 cm long, 1 cm diam.; disc descending; valves 4, rim level; seed dark brown, glossy, smooth, pyramidal but distorted by one curved face, hilum terminal. Flowers Sep.–Jan.
VVP, GipP, CVU, EGL, HSF, HNF, Strz, VAlp. Also NSW. A common stringybark of coastal ranges east and north-east from Melbourne. There is a markedly disjunct occurrence north of the Great Dividing Range, south-west of Tallangatta.
On near-coastal sands in Gippsland it can have a mallee habit and quite large fruits which may lead to confusion with E. baxteri, however, the coppice growth, which is scabrous for many nodes is diagnostic for E. globoidea.
Brooker, M.I.H.; Slee, A.V. (1996). Eucalyptus. In: Walsh, N.G.; Entwisle, T.J., Flora of Victoria Vol. 3, Dicotyledons Winteraceae to Myrtaceae, pp. 946–1009. Inkata Press, Melbourne.
 Spinning
Spinning