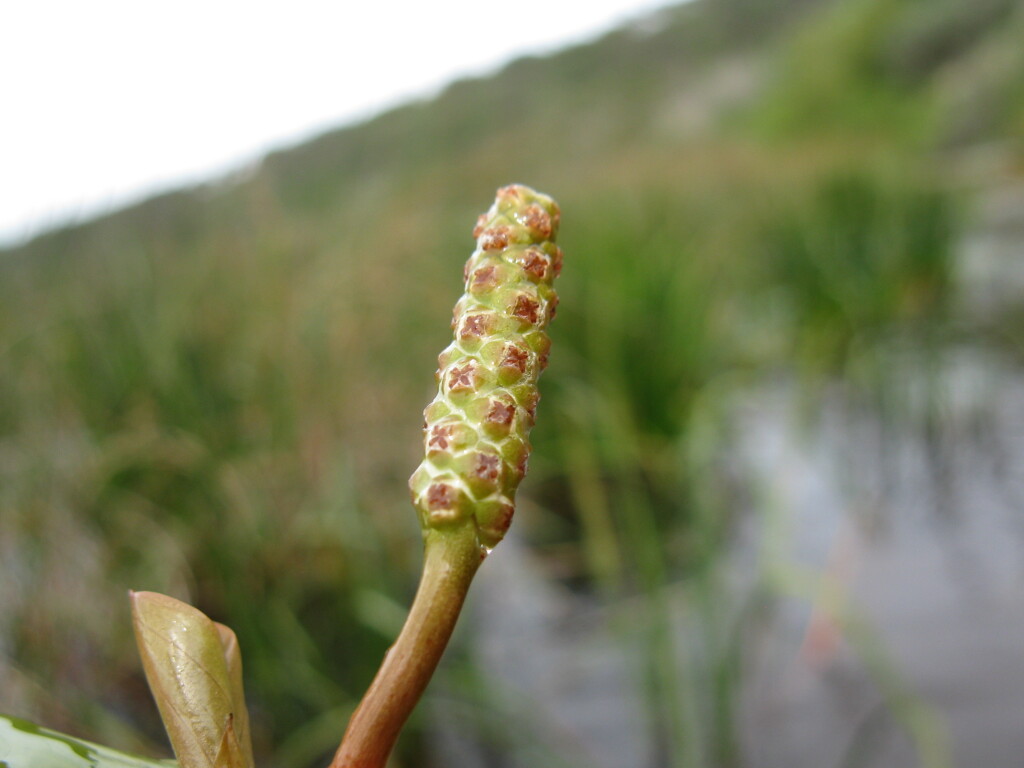
Potamogeton cheesemanii
A.Benn.Emergent herb; stem erect; branches flattened, up to c. 2 m long. Leaf sheath free, up to 4 cm long, soon torn; ligule absent. Submerged leaves different from emergent ones. Submerged leaves thin and translucent, sessile or very shortly petiolate; lamina lanceolate to elliptic, 5–10 cm long, 0.5–2.5 cm wide; base rounded to gradually tapered; margin flat or slightly undulate; apex obtuse to tapering; 5–12 principal longitudinal veins, with finer transverse secondary veins; distal submerged leaves more like emergent leaves, but with petiole much longer than for emergent leaves. Emergent leaves floating, ± thick and leathery, petiolate; lamina ovate to lanceolate, 1.5–5.0 cm long, 1.5–3.5 cm wide, dull; base rounded to cordate; apex obtuse to apiculate; margin flat; 10–20 principal longitudinal veins, with transverse secondary veins indistinct. Inflorescence c. 12–24 flowered. Infructescence 1.0–2.5 cm long (excluding non-fruiting part of axis). Fruiting carpels 2–3 mm long (including distal point), dorsal surface with a ± prominent, smooth to crenulate keel and 2 smooth lateral ridges that are sometimes low or not developed, distally with a ± straight to curved point up to c. 0.7 mm long. Flowers and fruits Sep.–Apr.
LoM, MuM, Wim, GleP, Brid, VVP, VRiv, RobP, MuF, GipP, OtP, WaP, CVU, DunT, EGL, HSF, HNF, Strz. Also WA, SA, NSW, Tas. Occurs in rivers, creeks, tarns and lagoons, on muddy substrates.
This species was previously treated as P. tricarinatus form II and form III. See notes under P. sulcatus and P. drummondii.
 Spinning
Spinning