Eucalyptus melliodora
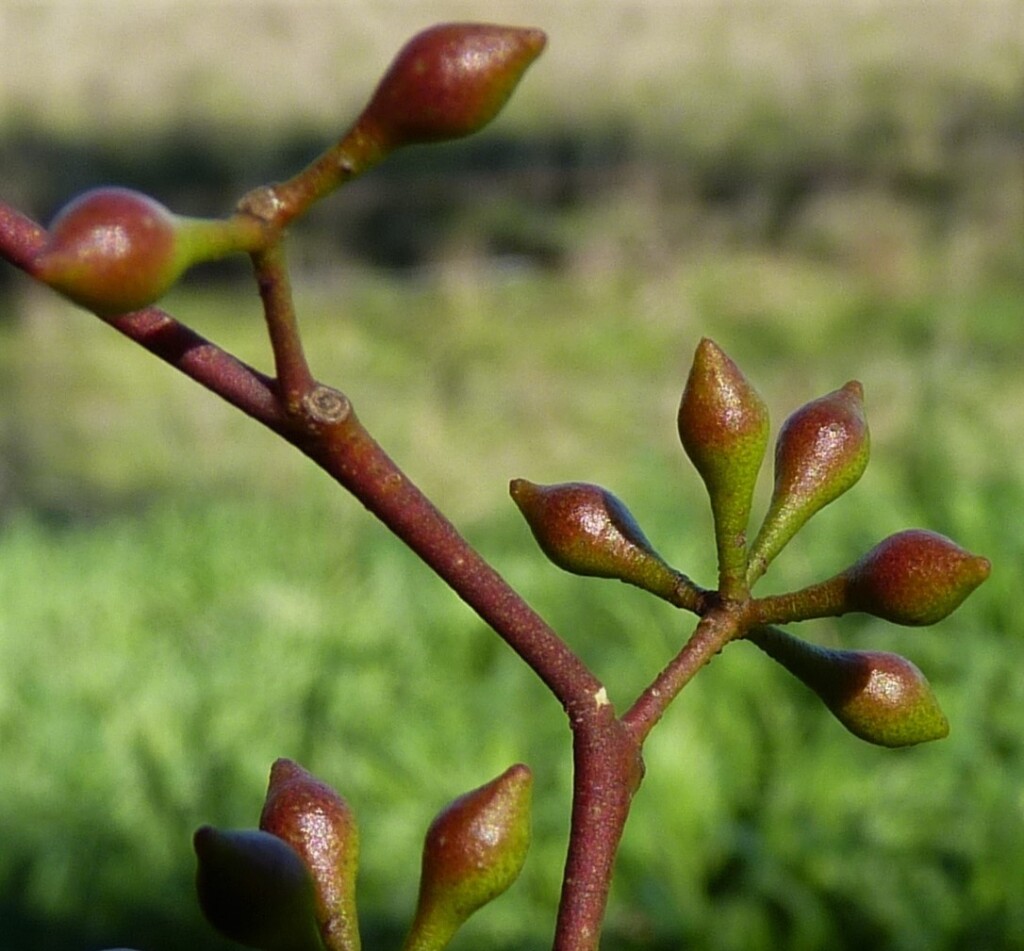
A.Cunn. ex Schauer Yellow BoxTree to 30 m tall, bark fibrous or with thin flakes of rough (often rust-coloured) bark held in variable amounts on trunk (sometimes entire trunk rough), rest of trunk and branches smooth, pale grey and yellow. Crown green or grey. Juvenile leaves petiolate, soon alternate, elliptic, to 11 cm long, 5 cm wide, dull, green or grey-green with distinct intramarginal veins well in from margin; adult leaves petiolate, lanceolate to narrowly lanceolate or falcate, 6–14 cm long, 0.8–1.5 cm wide, dull, green or grey with intramarginal vein well in from margin, reticulation dense, with numerous, island and intersectional oil glands. Inflorescences axillary, unbranched; peduncles to 1 cm wide, 7-flowered; buds shortly pedicellate, ovoid or clavate, to 0.7 cm long, 0.4 cm diam., no scar (2 opercula intact); operculum conical, sometimes rostrate; stamens inflexed with outer staminodes; anthers adnate, cuboid; ovules in 4 vertical rows; flowers white (rarely pink). Fruit hemispherical or truncate globose, 0.7 cm long, 0.7 cm diam.; staminal ring broad and usually deciduous; disc descending; valves 4 or 5; seed brown, irregularly ovoid and slightly flattened, surface shallowly reticulate, hilum ventral. Flowers Jul.–Feb.
LoM, MuM, Wim, VVP, VRiv, MuF, GipP, OtP, Gold, CVU, GGr, DunT, EGL, HSF, HNF, VAlp. Also Qld, NSW, AST. Widespread in Victoria from the Western District to the Gippsland Lakes and the upper Snowy River. And from the Grampians to the upper Murray River.
The natural distribution of Eucalyptus melliodora coincides with much of the moderate rainfall, cool temperate pastoral and cropping area of south-eastern Australia. It usually occupies the better soils, growing with E. blakelyi, E. camaldulensis and E. bridgesiana. It is distinguished from them by its scruffy, yellowish to dark brown, fibrous bark, dull, green or grey leaves with distinct intramarginal veins, and fruit with enclosed valves.
Brooker, M.I.H.; Slee, A.V. (1996). Eucalyptus. In: Walsh, N.G.; Entwisle, T.J., Flora of Victoria Vol. 3, Dicotyledons Winteraceae to Myrtaceae, pp. 946–1009. Inkata Press, Melbourne.
 Spinning
Spinning